Difference between high-speed steel vs high carbon steel
The hardness of high-speed steel reaches 65-70 HRC, while high carbon steel has a hardness of 60-65 HRC. High-speed steel is used for molds, and high carbon steel is used […]
The hardness of high-speed steel reaches 65-70 HRC, while high carbon steel has a hardness of 60-65 HRC. High-speed steel is used for molds, and high carbon steel is used for tools, mechanical parts, automotive components, bearings, etc. The price of high carbon steel is cheap, the hardness of high-speed steel is higher, and the wear resistance of high-speed steel is better.
High-speed steel (HSS) and high-carbon steel are both integral materials in tool manufacturing, but they serve different purposes and exhibit distinct properties. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right steel for specific applications in industrial production. Here’s a detailed comparison of their properties, applications, and cost-effectiveness.
Our factory business: We design, develop and produce powder metallurgy moulds, carbide parts, powder injection moulds, stamping toolings and precision mould parts. Whatsapp:+8618638951317. Email: [email protected],
I. Definitions and Properties
High-Speed Steel (HSS):
- Overview: HSS is a high-alloy, high-carbon tool steel known for its excellent hardness, heat resistance, and wear resistance. It is often used in tools that must withstand high temperatures and high-speed cutting, such as drills and milling cutters.
- Properties: High hardness, excellent wear resistance, and the ability to maintain these properties at high temperatures.
High-Carbon Steel:
- Overview: This steel type has a higher carbon content, enhancing its strength and hardness through heat treatment. It’s typically used where durability and wear resistance are required, such as in springs and high-strength wire.
- Properties: High strength and hardness, poor weldability, and limited cold deformation capabilities.
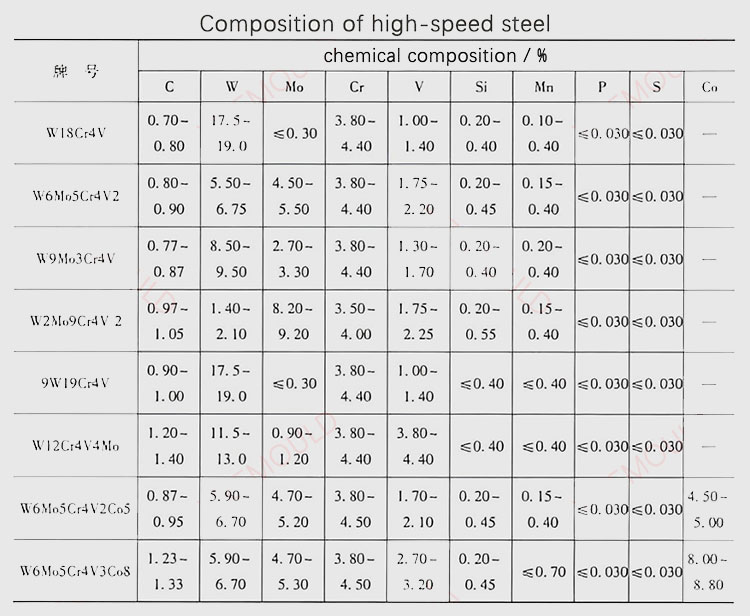
II. Chemical Composition and Heat Treatment
High-Speed Steel:
- Composition: Contains alloying elements like tungsten, molybdenum, vanadium, and chromium.
- Heat Treatment: Involves complex processes such as high-temperature annealing, quenching, and tempering to optimize hardness and toughness.
High-Carbon Steel:
- Composition: Higher percentage of carbon compared to other steel types, which significantly influences its mechanical properties.
- Heat Treatment: Requires careful heat treatment including annealing, normalizing, and quenching to achieve desired mechanical properties.
III. Performance Comparison
Hardness:
- High-Carbon Steel: Generally achieves a hardness of 60-65 HRC after heat treatment.
- HSS: Typically reaches hardness levels of 65-70 HRC, maintaining its hardness even under elevated temperatures.
Wear Resistance:
- High-Carbon Steel: Offers moderate wear resistance; however, it is more prone to wear and fatigue over time.
- HSS: Exhibits superior wear resistance, suitable for high-speed applications and those involving high loads.
IV. Applications
High-Speed Steel:
- Used predominantly in the manufacturing of cutting tools, taps, and dies.
- Ideal for applications requiring high endurance against heat and wear, such as in high-speed bearings.
High-Carbon Steel:
- Commonly used in the production of springs, knives, and other wear-resistant components.
- Suitable for applications where high strength and hardness are prioritized over toughness.
V. Price Comparison
- High-Carbon Steel: More affordable and widely available, making it a cost-effective option for many general applications.
- HSS: More expensive due to its alloying elements and complex production process, justified by its enhanced properties for specialized applications.
Conclusion
Both high-speed steel and high-carbon steel offer valuable properties for diverse industrial applications. The choice between HSS and high-carbon steel will largely depend on the specific requirements of the application, including the expected wear conditions, necessary hardness, and budget constraints. Engineers and designers must weigh these factors carefully to select the most appropriate material for their needs.
Related Articles:
This comprehensive comparison should assist in understanding when and why to choose either high-speed steel or high-carbon steel for specific industrial applications.

