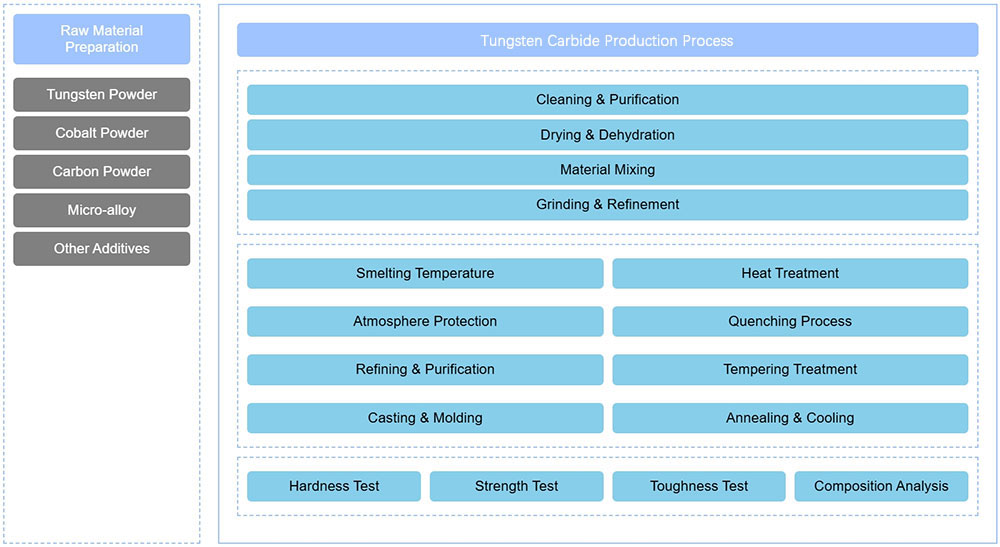
Tungsten Carbide Production Process
The production of tungsten carbide is a complex process that encompasses steps from raw material preparation and pre-treatment to smelting techniques and product performance testing. Each of these stages is […]
The production of tungsten carbide is a complex process that encompasses steps from raw material preparation and pre-treatment to smelting techniques and product performance testing. Each of these stages is further divided into various sub-processes. The preparation and pre-treatment of raw materials lay the foundation for the alloy’s performance, ensuring minimal impurities through precise proportioning and thorough cleaning. Subsequently, the smelting and casting processes demand precise control of smelting parameters and close monitoring of melt flow and solidification to produce uniform and dense castings. The heat treatment and machining stages further refine the microstructure of the alloy, enhancing its mechanical properties. In the quality inspection and performance testing stages, advanced analytical methods are employed to comprehensively evaluate the chemical composition, physical properties, and microstructure of the tungsten carbide alloy, ensuring that each batch of products meets high standards.
Our factory business: We design, develop and produce powder metallurgy moulds, carbide parts, powder injection moulds, stamping toolings and precision mould parts. Whatsapp:+8618638951317. Email: [email protected],
Selection and Proportioning of Raw Materials
In the preparation of tungsten carbide alloys, the selection of raw materials and precise proportioning are crucial foundational steps. The primary raw materials include high-purity tungsten powder, cobalt powder, and an appropriate amount of carbon powder, along with trace amounts of other alloying elements such as nickel, manganese, and silicon powders. These raw materials must strictly adhere to industry standards, be sourced from reputable suppliers, and undergo rigorous inspection and testing to ensure low impurity content and uniform particle size distribution, meeting the specific requirements of the alloy.
During the proportioning design phase, technicians must accurately calculate and mix the components according to the expected performance indicators, application scenarios, and production process requirements. For instance, to improve hardness and wear resistance, the tungsten content can be increased; while to enhance the toughness and machinability of the alloy, the cobalt content can be appropriately raised. Additionally, the influence of other elements on overall performance must also be considered.
Cleaning and Drying of Raw Materials
Before mixing, raw materials must undergo strict cleaning and drying pre-treatment processes. This step aims to thoroughly remove oil stains, oxides, and other harmful impurities from the raw material surfaces that may affect product quality. Cleaning operations often combine ultrasonic cleaning and chemical cleaning methods. Ultrasonic cleaning employs high-frequency vibrations to make the raw material particles collide and rub against each other, effectively removing stubborn dirt adhered to their surfaces. Chemical cleaning involves using specific solvents and catalysts under controlled temperature and pressure conditions to react with and dissolve contaminants.
After the cleaning process, the raw materials must be dried to prevent the presence of moisture, which could lead to defects such as gas pores or inclusions during smelting. Drying is usually carried out using hot air flow or vacuum drying equipment, with controlled temperature and time to ensure thorough removal of moisture while avoiding oxidation or agglomeration of raw materials due to over-drying. Only after such meticulous and careful raw material preparation can the resultant tungsten carbide alloy exhibit excellent quality and stable performance.
Alloy Smelting and Casting
Setting of Smelting Process Parameters
Alloy smelting is a critical step in the production of tungsten carbide alloys. Before beginning the smelting process, a series of key smelting parameters must be carefully set based on the characteristics of the raw materials, chemical composition, and equipment conditions. The smelting temperature is a core factor and must be set sufficiently high to ensure that all components in the raw materials are fully melted and thoroughly mixed to form a homogeneous alloy melt. An ideal smelting temperature also minimizes the formation of gas pores and inclusions, thereby enhancing the quality and performance of the final product.
In addition to smelting temperature, atmosphere control is also crucial. Oxidation and nitridation are major factors that degrade alloy performance and quality. Therefore, the composition and pressure of the furnace atmosphere must be precisely controlled. The smelting time must also be reasonably set according to the specific composition and desired performance of the alloy. Insufficient time may lead to incomplete melting or uneven mixing, causing segregation of components, while excessive time may result in excessive grain growth, negatively impacting the material’s mechanical properties and microstructure.
Smelting Process Control
During the smelting process, a series of meticulous operations and monitoring measures are required to ensure the homogeneity and thermal stability of the melt. Continuous stirring greatly facilitates the melting and mixing of raw materials.
Casting and Cooling
After completing the smelting process, the next crucial step is casting. During this stage, the high-temperature alloy melt is rapidly and precisely poured into molds that have been carefully designed and prepared in advance. The molds must not only possess excellent high-temperature resistance and precise dimensional control but also feature good thermal conductivity and moderate thermal expansion coefficients. This ensures uniform heat transfer and controlled cooling during the casting process. Common mold materials include sand molds, metallic molds, ceramic molds, or other specialized materials. Moreover, the casting speed and cooling rate must be tightly controlled.
Heat Treatment and Machining
Heat treatment is an essential technique for improving the microstructure and performance of tungsten carbide alloys. Depending on the specific application requirements of the product, various heat treatment processes can be employed for optimization, such as quenching, tempering, and annealing.
Quality Inspection and Performance Testing
Chemical Composition Analysis
Chemical composition analysis is a fundamental step in tungsten carbide alloy quality control. This involves accurately measuring the content of key elements like tungsten, cobalt, and nickel, while strictly controlling impurity elements such as sulfur and phosphorus.
Physical Performance Testing
Physical performance testing is a critical method for evaluating the properties of tungsten carbide alloys. These tests include, but are not limited to, hardness, tensile strength, yield strength, impact toughness, fatigue strength, and friction coefficient.
Microstructure Observation
Microstructure observation is an important means of understanding the internal structure and performance of tungsten carbide alloys. By analyzing the microstructure, insights can be gained into characteristics such as grain morphology, grain size, distribution, and phase composition.

